What Term Is Used to Describe Dna Replication and Why
In G1 phase Cdc6 and Cdt1 proteins load the MCM helicase onto the ORC. Special molecules break the weak hydrogen bonds between bases which are holding the two strands together.

Extensive Coevolution In Dna Replication Genes Cartoon Representation Download Scientific Diagram
The DNA is unwound and unzipped.

. The helix structure is unwound. The term used to describe this phenomenon is _____ DNA replication. In the replicated molecules each has one parent strand and one newly-synthesized daughter strand.
The central enzyme involved is DNA polymerase which catalyzes the joining of deoyribonucleoside 5-triphosphates dNTPs to form the growing DNA chain. What direction does DNA replication follow. The pairing of C with G exemplifies the definition of.
The term semi-conservative used to describe DNA replication means that. DNA replication is an essential part of cell division as it ensures that each new cell has the same genetic information. The term used to describe two DNA strands that run in opposite directions from each other is.
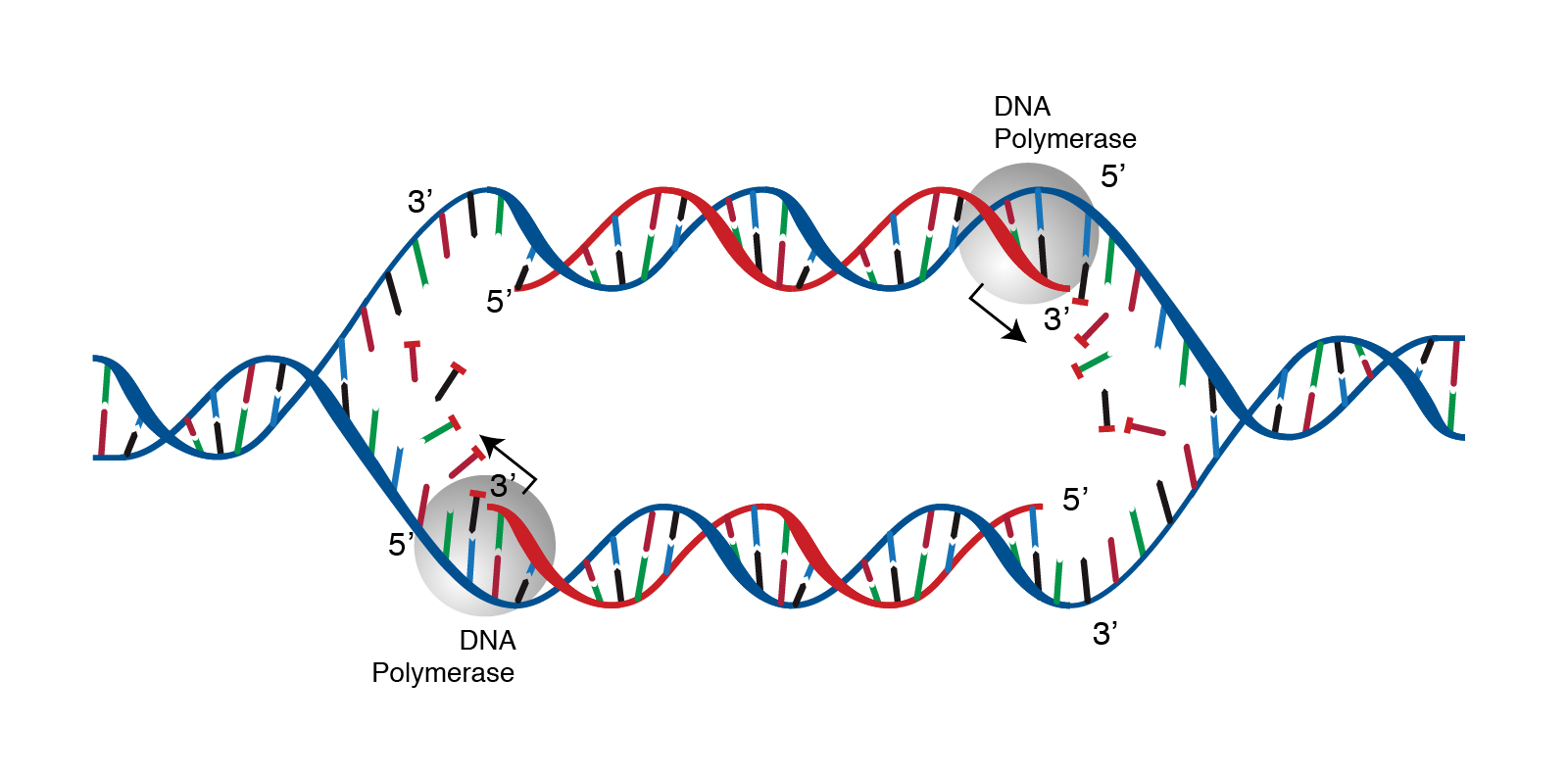
The area of a DNA molecule where the replication process takes place is often referred to as a replication fork Explain why you think this term is used to describe this location. DNA replication in prokaryotes is bidirectional from one origin of replication whereas eukaryotic replication is bidirectional from multiple origins of replication on each chromosome. However DNA replication is much.
The process of DNA duplication is called DNA replication. The fragments are bound together by the enzyme DNA ligase in order to complete replication in the lagging strand of DNA. In eukaryotic cells such as animal cells and plant cells DNA replication occurs in the S phase of interphase during the cell cycle.
Refers to the newly synthesized strand of DNA that is copied via the addition of complementary nucleotides from one strand of pre-existing DNA during DNA replication. Cancer The enzyme that positions complementary nucleotides on growing daughter strands during DNA replication is called DNA helicase If an error occurs during the replication process that error would be passed on to all subsequent daughter strands resulting in in the organism wasteful Over time this could cause a sequence of DNA to. DNA replication is probably one of the most amazing tricks that DNA does.
The central enzyme involved is DNA polymerase which catalyzes the joining of deoxyribonucleoside 5-triphosphates dNTPs to form the growing DNA chain. This process takes us from one starting molecule to two daughter molecules with each newly formed double helix containing one new and one old strand. The 13-mer and 9-mer consensus sequences that are part of oriC have been maintained by natural selection because they have essential functional roles in replication initiation.
Why is an RNA polymerase necessary at the start of DNA replication. DNA replication occurs in a series of five steps. I am referring to the strand being synthesized 8.
It is also necessary for evolution and immune system response. Replication occurs in three major steps. ORC recognizes and binds to the origin.
Cells Can Replicate Their DNA Precisely. The points where the DNA first are opened are called replication. How does DNA Polymerase III differ from DNA Polymerase I.
We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. The opening of the double helix and separation of the DNA strands the priming of the template strand and the assembly of the new DNA segment. DNA replication Stage one.
To accomplish this each strand of existing DNA acts as a template for replication. The two arms of each Y Initially the simplest mechanism of DNA replication seemed to be the continuous growth of both new strands nucleotide by nucleotide at the replication fork as it moves from one end of a DNA. Again keeping with the similarity to the centromere this metaphor also has been used to describe the building of the kinetochore on the centromere.
DNA Helicase The enzyme responsible for separating the two strands of DNA in a helix so that they can be copied during DNA replication. Replication is the term used to describe the process of copying DNA. As discussed in Chapter 3 DNA replication is a semiconservative process in which each parental strand serves as a template for the synthesis of a new complementary daughter strand.
What term is used to describe the the process of copying DNA. It is because of the DNA Replication process that takes place during the S-phase synthetic phase of the cell division mitosis or meiosis in each and every cell. Replication is the process by which a double-stranded DNA molecule is copied to produce two identical DNA molecules.
The reason why DNA replication occur only in 5 to 3 direction is. Where does transcription take place. Responses can be used more than once.
Does DNA polymerase use the template strand or the daughter strand to. One of these is called the leading strand and it runs in the 3 to 5 direction and is replicated continuously because DNA polymerase works antiparallel building in the 5 to 3 direction. DNA replication is regulated in the cell cycle in the following manner Figure 1b.
Explain what the term antiparallel means in terms of DNA replication. DNA replication is one of the most basic processes that occurs within a cell. DNA replication uses each parent strand as a template to produce a new daughter strand.
What term is used to describe DNA replication. And we start out from a single cell and we end up with trillions of cells. Replication follows several steps that involve multiple proteins called replication enzymes and RNA.
DNA replication is the process of producing two identical copies of DNA in which each template for the synthesis of a new complementary daughter strand. DNA replication is semiconservative meaning that each strand in the DNA double helix acts as a template for the synthesis of a new complementary strand. An active zone of DNA replication moves progressively along a replicating DNA molecule creating a Y-shaped DNA structure known as a replication fork.
If you think about it each cell contains all of the DNA you need to make the other cells. Describe why replication of DNA moves 5-3 and the trombone model is needed to explain the concerted movement of the replisome. FINISHING REPLICATION z After replication of a circular chromosome is complete the resulting daughter DNA molecule remains linked together as catanenes two circles remains linked together as catanenes two circles linked together like a chain z The two molecules are separated by the action of z The two molecules are separated by the action of type II.
View the full answer. DNA Ligase The enzyme responsible for sealing together breaks or. In DNA replication the _____ strand is made discontinuously in the direction opposite to the movement of the replication fork.
Both strands are new DNA DNA is not replicated Both strands are. Initiation at the origin of replication unwinding to expose the strands synthesis on both strands with many enzymes adding.

Dna Replication Leading Strand Vs Lagging Strand Okazaki Fragments Youtube

Dna Replication Steps Diagram Expii
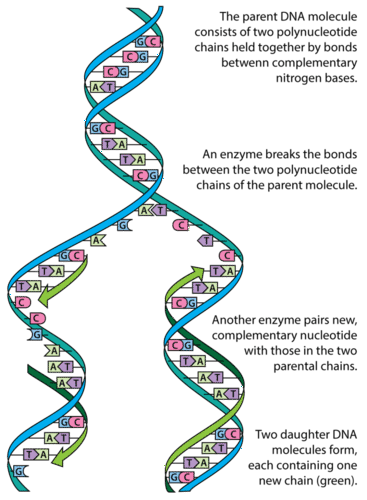
Dna Replication Advanced Ck 12 Foundation
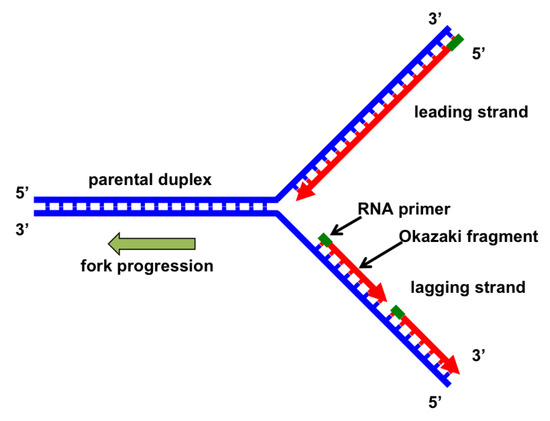
Genes Free Full Text The Replication Fork Understanding The Eukaryotic Replication Machinery And The Challenges To Genome Duplication Html
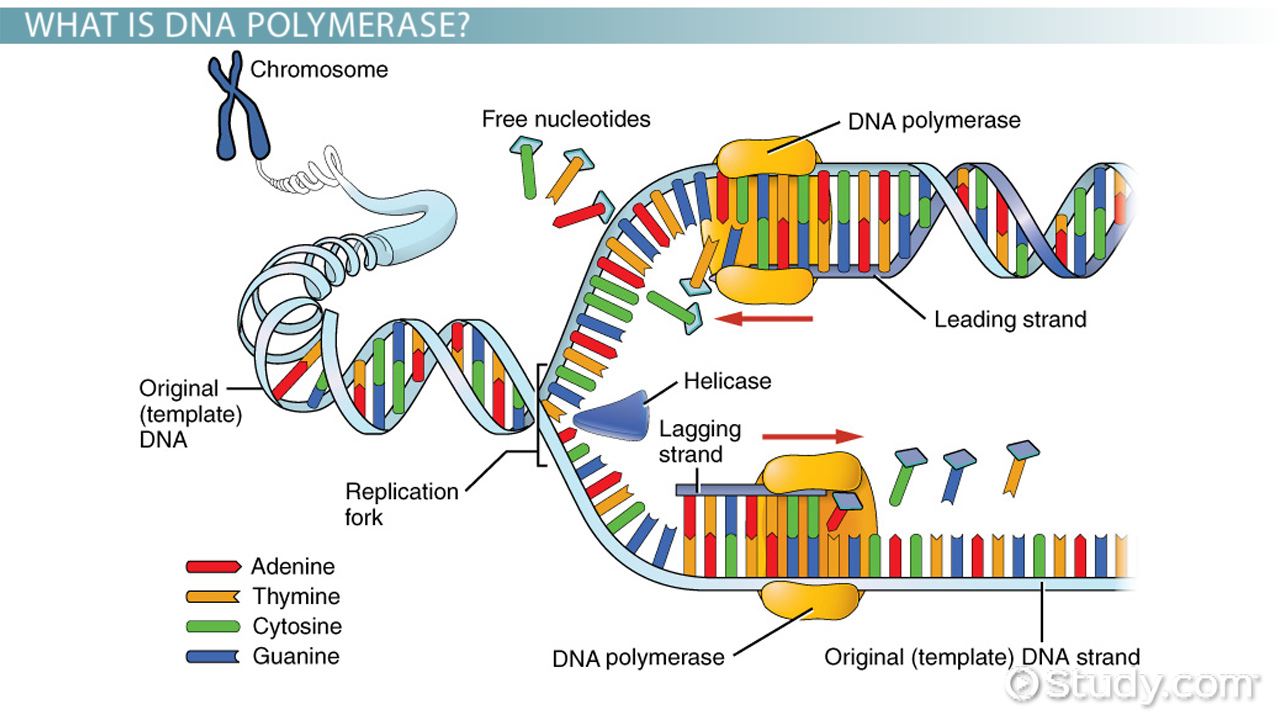
Topic 2 7 Dna Replication Transcription And Translation Amazing World Of Science With Mr Green

Molecular Events Of Dna Replication Learn Science At Scitable
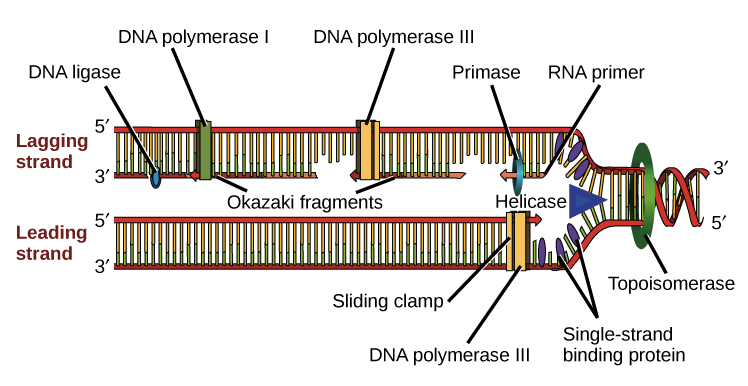
Molecular Mechanism Of Dna Replication Article Khan Academy

What Are The Steps Of Dna Replication

Dna Replication Structure Stages Of Replication Teachmephyiology
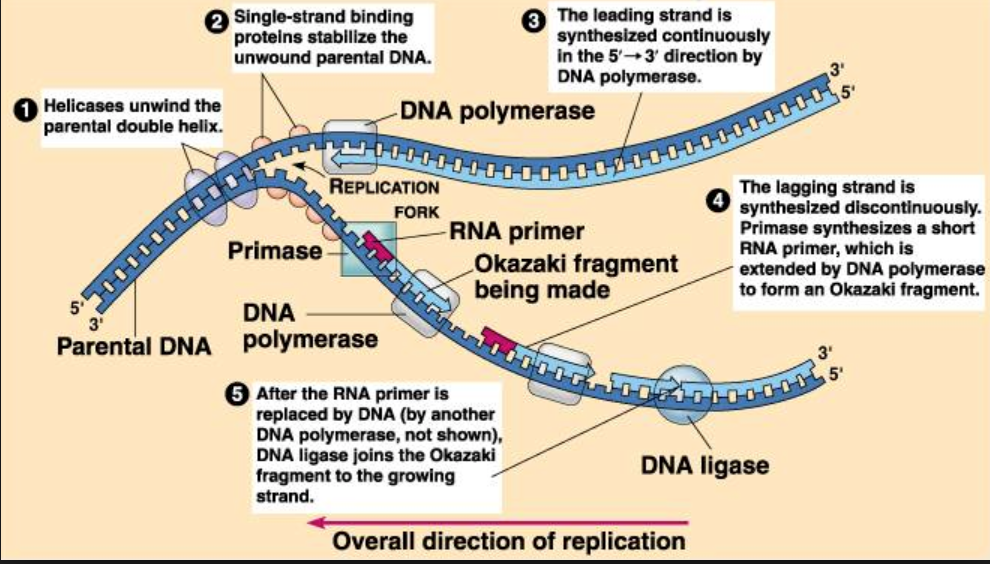
What Is The Primer Used For Dna Replication Socratic
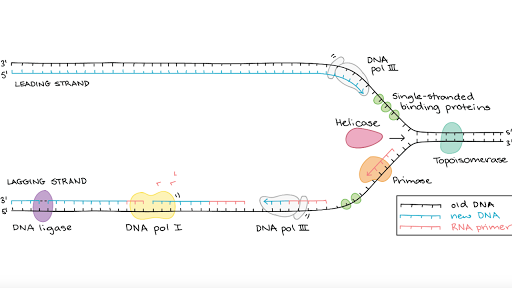
Molecular Mechanism Of Dna Replication Article Khan Academy

Dna Replication The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary

Dna Replication Checkpoint Dna Synthesis Learn Science At Scitable
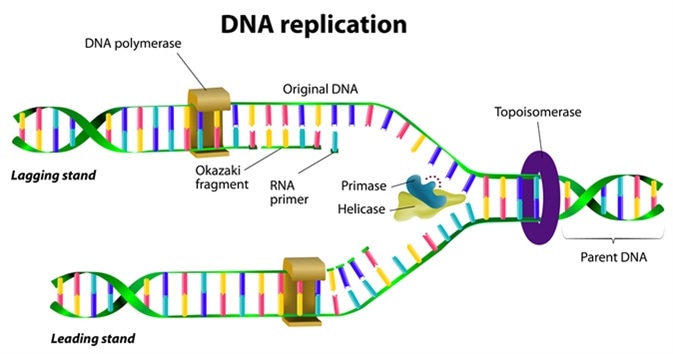


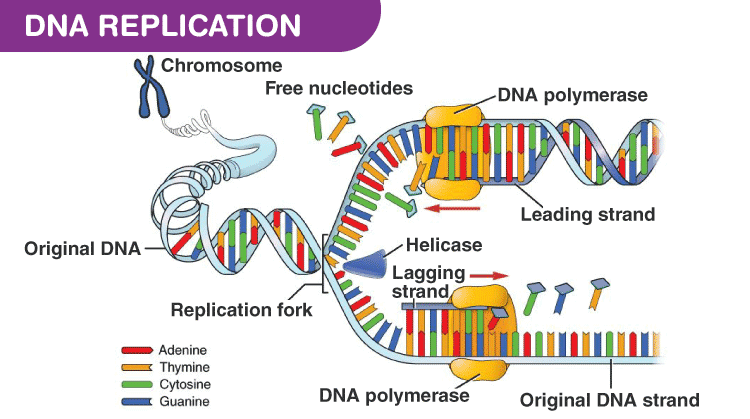
Comments
Post a Comment